Revolutionizing color
through resonance
News & Release
{category_name}
Concept
Resonance Color makes the world more Sustainable.
Color not only gives us convenience, but also enriches our lives through art, clothing, and everyday items. However, some artificial colorants use harmful chemicals. In addition, since many colorants are used, their weight reduces the fuel efficiency of mobility, and the painting process emits a lot of CO₂.
“Resonance Color” with silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) is a completely new color technology that uses an optical phenomenon called Mie resonance. It overturns this conventional wisdom of the color industry.Through our technology, we will contribute to an environmentally friendly and prosperous future society.
About
What Mie-Resonant
Silicon Makes Possible
Resonance Condition
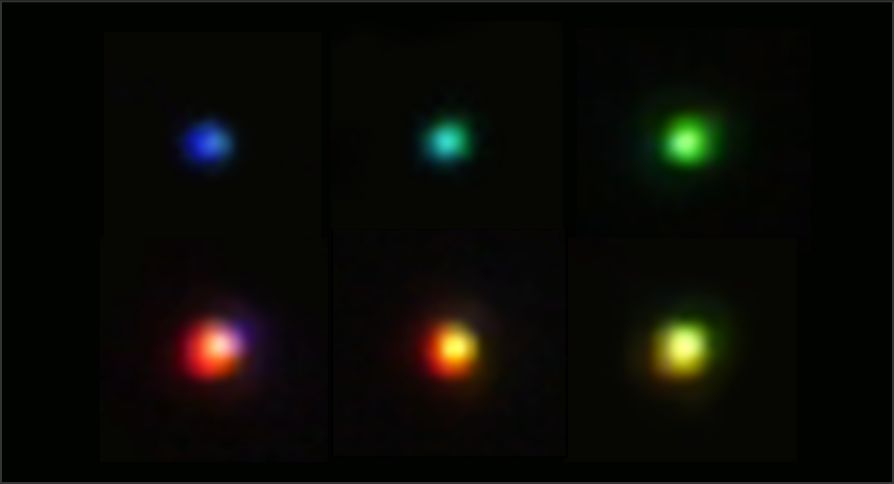
Mie resonance is a phenomenon in which light strongly interacts with nanoparticles.By tuning the size of 100 nm-scale silicon spheres, specific wavelengths of light can be selectively enhanced and scattered—enabling structural coloration with a single particle.
In contrast to conventional structural coloration, which typically requires complex, multidimensional architectures such as thin films or colloidal crystals, our approach achieves vivid color through individual silicon nanoparticles alone.
Furthermore, by simply varying the particle size, full-color expression—blue, green, and red—can be realized using just one material: silicon.
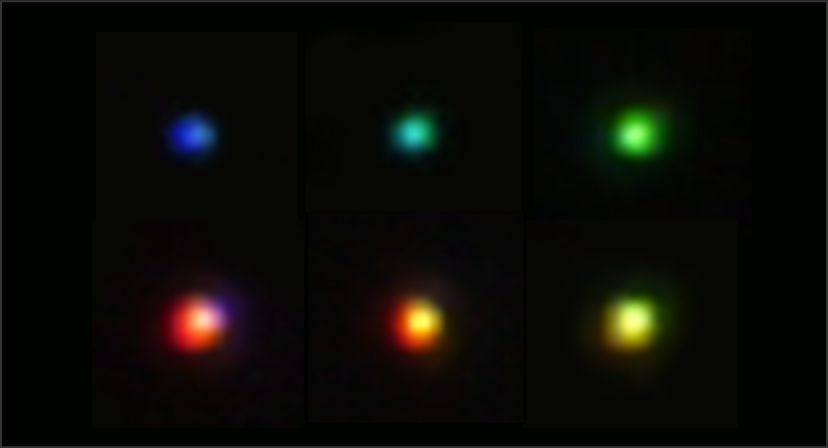

Dark-field image of SiNPs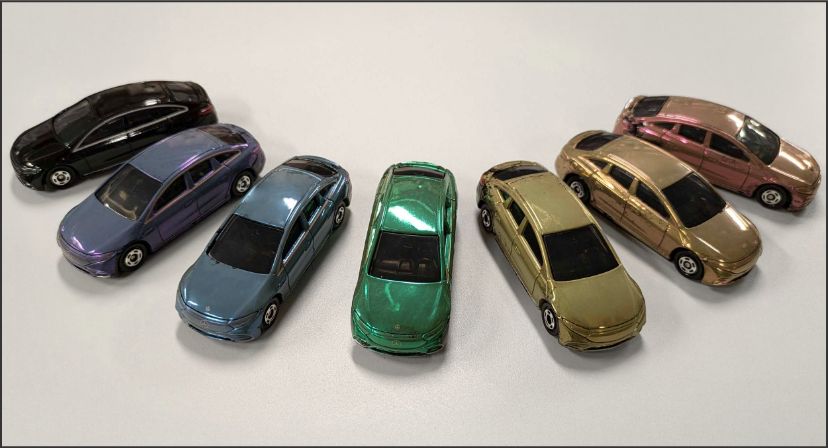 
3D metal toy model coated with SiNPs
Vivid color achieved with <200 nm coating thickness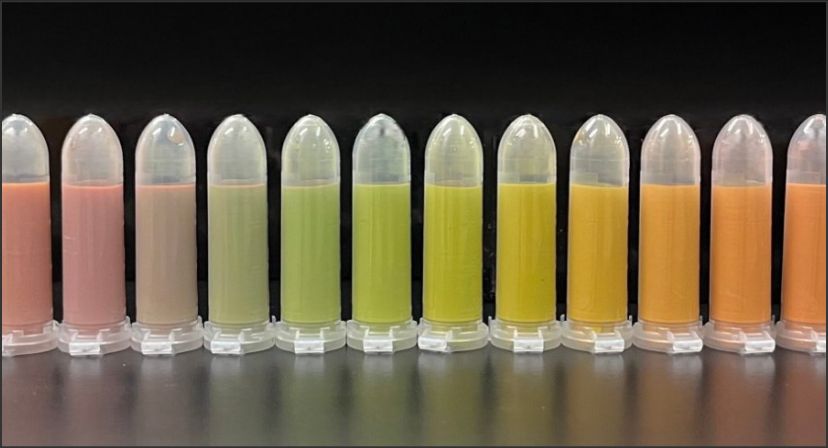
SiNPs ink (0.1wt% of SiNPs)
Application

Swipe sideways to browse
For more information

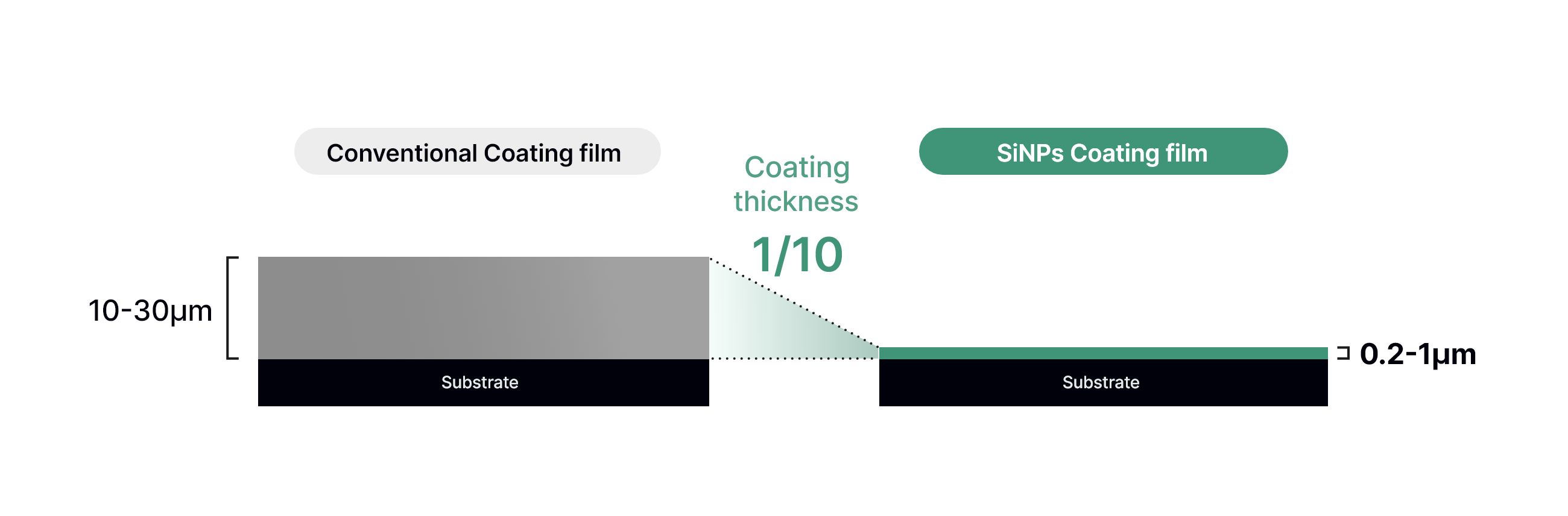
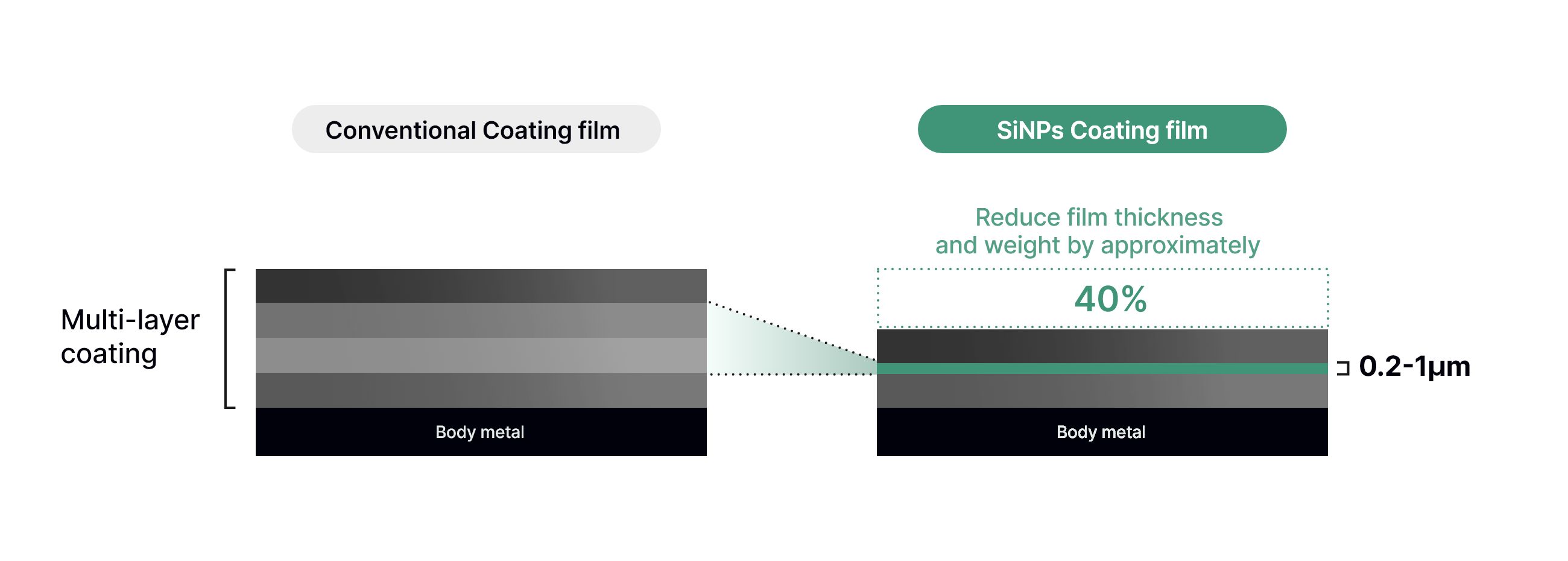
Ultra Light & Thin
High scattering efficiency and opacity enable ultra thin films.
The coating weight is only 0.2-0.4 g/m2, the lightest in the world.
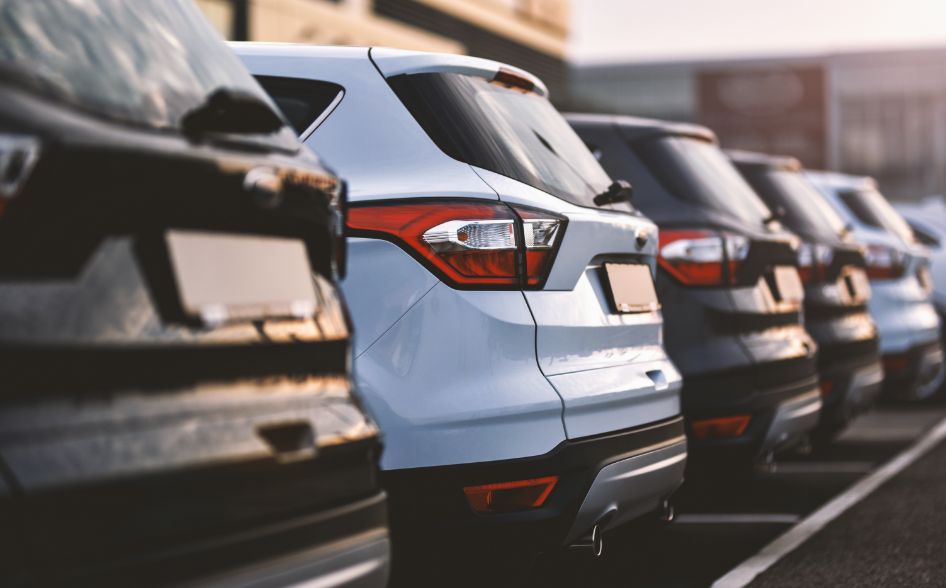
Case: Application to
automobile body
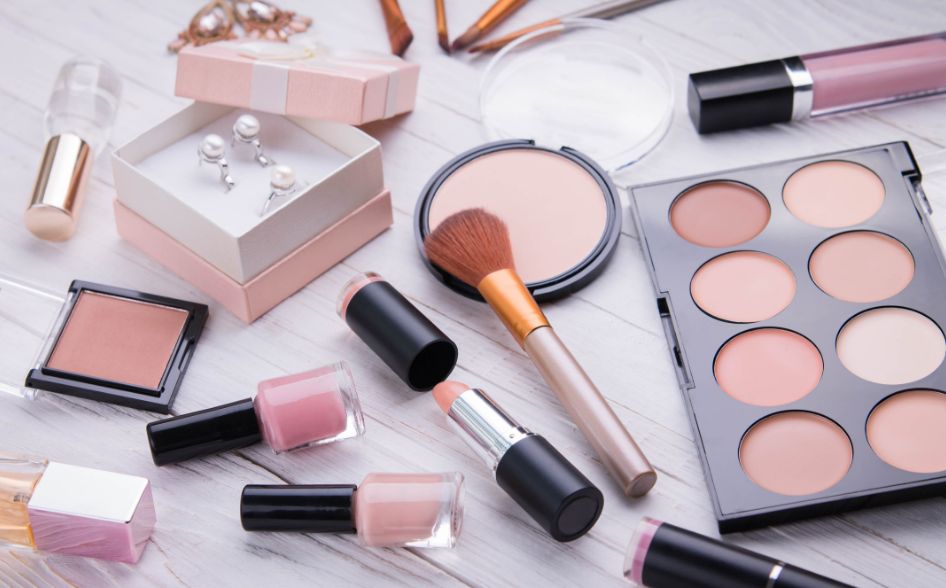
SiNPs can give benefits to not only automobile body
but cosmetics such as foundation.

Weather Resistance
High functionality unique to silicon
-
01
High Temperature
ResistanceNo change at temperatures
below 500℃. -
02
Ultraviolet Cut
Cutting ultraviolet rays over an area 3 times the cross-sectional area of SiNPs.
-
03
Chemical Resistance
Chemically stable and resistant
to acids and alkalis.

Non Fading
Structural colors, incl. resonance colors,
do not fade in principle unlike organic pigments.
-
Pigment Color
Fading due to ultraviolet rays (UV) and high temperature

-
Structural Color
Non-fading during 100 million years

Sustainable
Silicon is abundant in resources,
the second most abundant element (26%) in the earth’s crust.
| Element | O | Si | Al | Fe | Ca | Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clark number (wt%) |
49.5 | 25.8 | 7.5 | 4.7 | 3.4 | 2.6 |
One raw material can be used to produce full color,
facilitating recycling through mono-materialization.

Safe & Secure
Affinity for the human body
Silicon is an element that is ingested from food and contained in the human body.
| Element | in a 70 -kg person |
|---|---|
| oxygen | 43 kg |
| carbon | 16 kg |
| hydrogen | 7 kg |
| nitrogen | 1.8 kg |
| calcium | 1.0 kg |
| phosphorus | 780 g |
| potassium | 140 g |
| sulfur | 140 g |
| sodium | 100 g |
| chlorine | 95 g |
| magnesium | 19 g |
| iron | 4.2 g |
| fluorine | 2.6 g |
| zinc | 2.3 g |
| silicon | 1.0 g |
Affinity for industry
Silicon is widely used in semiconductors, electronic devices, solar panels, etc.
These can be reused as raw materials.
















